The VA home loan is a government-backed mortgage for Veterans or active service members that comes with significant financial benefits, including purchasing without a down payment and no out-of-pocket costs. For the vast majority of military borrowers, VA loans are the most powerful and cost-effective mortgage program on the market.
But there are certainly times when a VA loan isn't the best answer, and a conventional loan may be a better option.
A conventional loan is a type of mortgage that isn't insured by the federal government and adheres to the standards of government-sponsored enterprises Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. It's a popular choice for most homebuyers who either don't meet the eligibility requirements for other mortgage types or who can afford a larger down payment.
Let’s break down the difference between VA loans and conventional loans and when one option may be more favorable than the other.
Conventional vs. VA Loan Volume
For 2024, over 4,750,000 conventional loans were originated compared to around 490,000 VA loans.
Based on the most recently updated HMDA data as of 2025.
Differences Between VA and Conventional Loans
Choosing between a VA loan or a conventional loan can be a difficult decision. While some VA loan requirements are similar to conventional, there are notable distinctions between the two.
Below is a table outlining the essential factors when comparing VA loans to conventional loans.
| Comparison Factor | VA Loans | Conventional Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Borrower must be a Veteran, service member or surviving spouse with valid COE | No special requirements |
| Dow Payment | $0 | 3% to 20% of loan amount |
| Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) | No PMI | PMI for mortgages with less than 20% down |
| Interest Rates | Typically lower than conventional | Typically higher than the VA |
| Credit Score | Not set by the VA, but lenders often required at least a 620 FICO | Typically a 620 FICO minimum |
| Property Type | Primary residence only | Primary, secondary, investment and vacation properties |
| Program Fees | VA Funding Fee (1.25% to 3.3% of loan amount) | No program fees |
Let’s explore the specifics of each factor and understand situations when one loan type might be more favorable than the other.
Eligibility
The most significant difference is who can use each loan type. VA loans are for Veterans, active duty military and surviving spouses with a valid Certificate of Eligibility (COE). Those who don't meet the basic service requirements won't be able to get a VA loan.
Conventional loans don't have any special borrower requirements. Anyone with the credit and finances to get a conventional loan may be eligible.
Takeaway: If you are a Veteran or active duty service member, it's usually best to use your VA loan benefits.
Down Payment
The most prominent benefit of the VA loan is the down payment requirements or lack thereof.
Most VA borrowers don't need a down payment to secure financing. If a VA borrower does need a down payment, it's typically due to diminished VA loan entitlement.
Conversely, conventional loans often require a down payment of at least 5% (in some cases, it may be 3%). According to the FED, the average home sale price in Q2 of 2023 was $503,000. A conventional borrower with a 5% down would need to bring more than $25,150 to closing for their down payment.
Takeaway: Choose a VA loan if you don’t have funds saved for a down payment.
Private Mortgage Insurance
VA loans do not require private mortgage insurance (PMI), saving the borrower thousands over the life of the loan.
Conventional loans with less than 20% down do require PMI. Depending on home price, credit score and other factors, PMI can easily run $150 to $200 monthly. But if you can afford to make a 20% down payment, conventional loans do not require PMI.
PMI protects the lender if you default on your loan and typically falls off after you reach 80% loan-to-value (the equivalent of placing 20% down).
To put that in perspective, the chart below illustrates how much individuals would need to pay to avoid PMI on a conventional loan.
Avoiding PMI for Conventional Loans
| Home Price | Down Payment Needed |
|---|---|
| $250,000 | $50,000 |
| $350,000 | $70,000 |
| $450,000 | $90,000 |
Takeaway: If you're unable to afford a 20% down payment for a conventional loan and want to avoid PMI, a VA loan is your best choice.
Are VA Rates Better Than Conventional?
VA loan rates are often the lowest rates on the market. According to the mortgage data and analytics company Optimal Blue, VA loan rates were .47% lower on average than conventional in 2024.
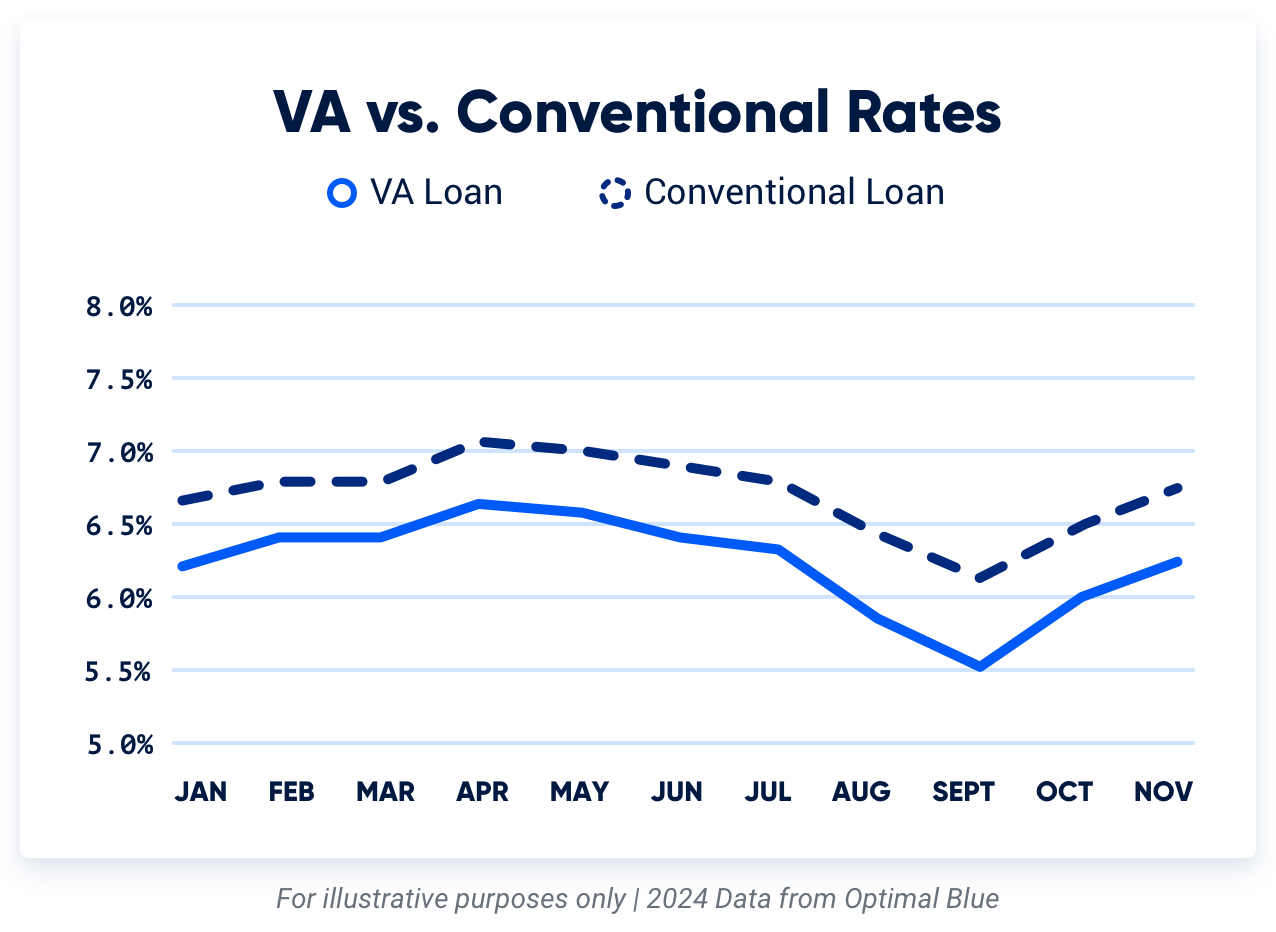
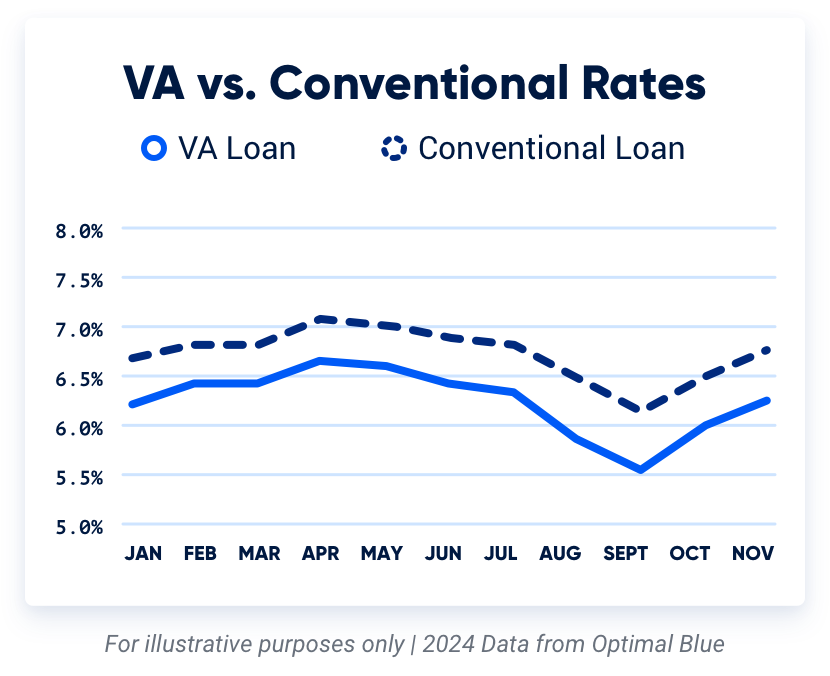
A .47% difference in rate may sound small, but that can equal tens of thousands in interest savings over the life of the mortgage.
VA loans are backed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, giving lenders the confidence to extend more favorable rates to borrowers who may not have perfect credit.
Takeaway: Over the last year, VA interest rates were slightly lower than conforming rates. However, interest rates largely depend on your financial situation.
Credit Score
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) does not set a credit score minimum on VA loans, but most lenders do. Just like conventional loans, VA lenders typically like seeing a 620 or better mortgage credit score. However, some VA lenders will accept credit scores as low as 580.
You may still be eligible for a VA loan with a bad credit score if you meet certain “compensating factors,” such as a great debt-to-income ratio, long-term employment history or a healthy record of previous home ownership. Another option is working with a credit consultant to improve your credit score.
Takeaway: It may be easier to qualify for a VA loan than a conventional loan if your credit score is below 620.
Property Type
A significant difference between VA and conventional loans is that VA loans are only for primary residences. The primary residency requirement doesn't rule out duplexes or fourplexes, but to use a VA loan, you must intend to live in the property you purchase.
Conversely, conventional loans are available to purchase primary residences, vacation homes, rental properties and other investment properties.
Takeaway: Choose a conventional loan if the home will solely serve as a vacation, rental or investment property.
Program Fees
VA loans come with what's known as the VA Funding Fee. The fee ranges from 1.25% to 3.3% and is applied to every VA purchase and refinance loan. The VA Funding Fee is often rolled into the entire loan amount to make for a true $0-down loan.
Conventional loans do not have any unique fees like the VA Funding Fee.
Takeaway: VA Funding Fee exemptions are available under certain circumstances. However, a conventional mortgage is better for avoiding program fees.
Additional Requirements to Consider
Another aspect that separates VA loans from traditional mortgages is the VA’s Minimum Property Requirements (MPRs). VA loan properties must meet certain criteria to ensure the home is safe, sanitary and structurally sound.
Also, VA loans don’t have loan limits if you have full VA entitlement, but conventional mortgages always do. These limits are set by each county, with most counties setting their limit at $806,500 for a single-family property.
Lastly, VA mortgages have a cap on closing costs and limit what borrowers can pay for through “non-allowable fees.” This can make VA loans more financially favorable if you’re on a tight budget.
Are VA Loans More Strict Than Conventional?
Not necessarily. VA loans typically have more lenient qualification criteria compared to conventional loans, such as flexible credit score requirements, lower interest rates and no private mortgage insurance required. However, VA loans must adhere to the specific property guidelines set by the VA. At times, this can restrict the range of property options for VA buyers.
In today’s competitive market, appraisal contingencies are worth noting. A number of conventional loans are forgoing this step to enhance the appeal of their offers. However, VA loans require a VA appraisal to ensure that properties meet established standards. The inability to waive this contingency can sometimes place VA buyers at a disadvantage in highly competitive housing markets.
Benefits of a VA Loan vs. Conventional
While VA loans and conventional loans have their own strengths, there are a few advantages a VA loan offers that are very helpful for homebuyers. According to our 2022 Veteran Homebuyer Report, here are the top reasons Veterans choose the VA loan:
- No down payment: If you are eligible for full entitlement to VA benefits, no down payment is required. This can help you achieve homeownership faster since you do not have to save for a hefty down payment.
- Competitive interest rates: VA loan interest rates are typically lower than conventional and can help save money over the life of the loan. According to ICE Mortgage Technology, VA loans have had the lowest average 30-year fixed rate on the market for the last six years.
- Closing cost and fee limits: VA loans have certain fees buyers cannot pay called “non-allowable fees” and allow up to 4% in seller concessions.
- VA Funding Fee exemptions: Certain individuals may be exempt from paying the VA Funding Fee. This fee is usually 2.15% of the loan, so not having to pay it is a major advantage.
- No private mortgage insurance: Not having to pay mortgage insurance for the life of the loan can save a homeowner thousands of dollars in the long run. This is an extra expense VA homebuyers don’t have to worry about.
Is a VA Loan Better Than a Conventional Mortgage?
Deciding if a VA loan or conventional loan is better comes down to your own situation and needs.
A VA loan might be the best option if you lack funds for a down payment or your debt-to-income ratio is on the higher side. Although there is a one-time VA Funding Fee, you won’t have the recurring expense of private mortgage insurance.
A conventional loan might be better if you're able to make a 20% down payment and avoid the need for mortgage insurance. If you want to buy a second residence or investment property, a conventional loan is your best option due to VA occupancy requirements.
No matter what your homebuying goals are, Veterans United is here to help. Talk with a VA home loan expert to get a complete comparison for your unique homebuying journey.
How We Maintain Content Accuracy
Our mortgage experts continuously track industry trends, regulatory changes, and market conditions to keep our information accurate and relevant. We update our articles whenever new insights or updates become available to help you make informed homebuying and selling decisions.
Current Version
Apr 3, 2025
Written ByChris Birk
Minor update to originations data to add updated 2024 Home Mortgage Disclosure Act (HMDA) data.
Dec 13, 2024
Written ByChris Birk
Updated loan limits to 2025 numbers: $806,500 for the standard limit and $1,209,750 in higher cost areas.
Veterans United often cites authoritative third-party sources to provide context, verify claims, and ensure accuracy in our content. Our commitment to delivering clear, factual, and unbiased information guides every piece we publish. Learn more about our editorial standards and how we work to serve Veterans and military families with trust and transparency.
- Average Sales Price of Houses Sold for the United States, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Economic Data.
- Home Mortgage Disclosure Act, 2024. For 2023, over 4,500,000 conventional loans were originated compared to around 377,000 VA loans.
- Optimal Blue Mortgage Market Indices. VA loan rates were .47 percent lower on average than conventional in 2024.
Related Posts
-
 What is Credit and Why It’s ImportantDiscover why credit matters when buying a house. Learn how a strong score unlocks lower rates, better loans, and more financial freedom.
What is Credit and Why It’s ImportantDiscover why credit matters when buying a house. Learn how a strong score unlocks lower rates, better loans, and more financial freedom. -
 Home Inspection for VA Loans: Guidelines and ChecklistLearn about the purpose of a home inspection, common issues and how a home inspection differs from the VA appraisal.
Home Inspection for VA Loans: Guidelines and ChecklistLearn about the purpose of a home inspection, common issues and how a home inspection differs from the VA appraisal.


